Chapter 11: Transform Again, Naturally
We are about to discuss natural transformations in the context of practical utility in every day code. It just so happens they are a pillar of category theory and absolutely indispensable when applying mathematics to reason about and refactor our code. As such, I believe it is my duty to inform you about the lamentable injustice you are about to witness undoubtedly due to my limited scope. Let's begin.
Curse This Nest
I'd like to address the issue of nesting. Not the instinctive urge felt by soon to be parents wherein they tidy and rearrange with obsessive compulsion, but the...well actually, come to think of it, that isn't far from the mark as we'll see in the coming chapters... In any case, what I mean by nesting is to have two or more different types all huddled together around a value, cradling it like a newborn, as it were.
Right(Maybe('b'));
IO(Task(IO(1000)));
[Identity('bee thousand')];
Until now, we've managed to evade this common scenario with carefully crafted examples, but in practice, as one codes, types tend to tangle themselves up like earbuds in an exorcism. If we don't meticulously keep our types organized as we go along, our code will read hairier than a beatnik in a cat café.
A Situational Comedy
// getValue :: Selector -> Task Error (Maybe String)
// postComment :: String -> Task Error Comment
// validate :: String -> Either ValidationError String
// saveComment :: () -> Task Error (Maybe (Either ValidationError (Task Error Comment)))
const saveComment = compose(
map(map(map(postComment))),
map(map(validate)),
getValue('#comment'),
);
The gang is all here, much to our type signature's dismay. Allow me to briefly explain the code. We start by getting the user input with getValue('#comment') which is an action which retrieves text on an element. Now, it might error finding the element or the value string may not exist so it returns Task Error (Maybe String). After that, we must map over both the Task and the Maybe to pass our text to validate, which in turn, gives us back Either a ValidationError or our String. Then onto mapping for days to send the String in our current Task Error (Maybe (Either ValidationError String)) into postComment which returns our resulting Task.
What a frightful mess. A collage of abstract types, amateur type expressionism, polymorphic Pollock, monolithic Mondrian. There are many solutions to this common issue. We can compose the types into one monstrous container, sort and join a few, homogenize them, deconstruct them, and so on. In this chapter, we'll focus on homogenizing them via natural transformations.
All Natural
A Natural Transformation is a "morphism between functors", that is, a function which operates on the containers themselves. Typewise, it is a function (Functor f, Functor g) => f a -> g a. What makes it special is that we cannot, for any reason, peek at the contents of our functor. Think of it as an exchange of highly classified information - the two parties oblivious to what's in the sealed manila envelope stamped "top secret". This is a structural operation. A functorial costume change. Formally, a natural transformation is any function for which the following holds:
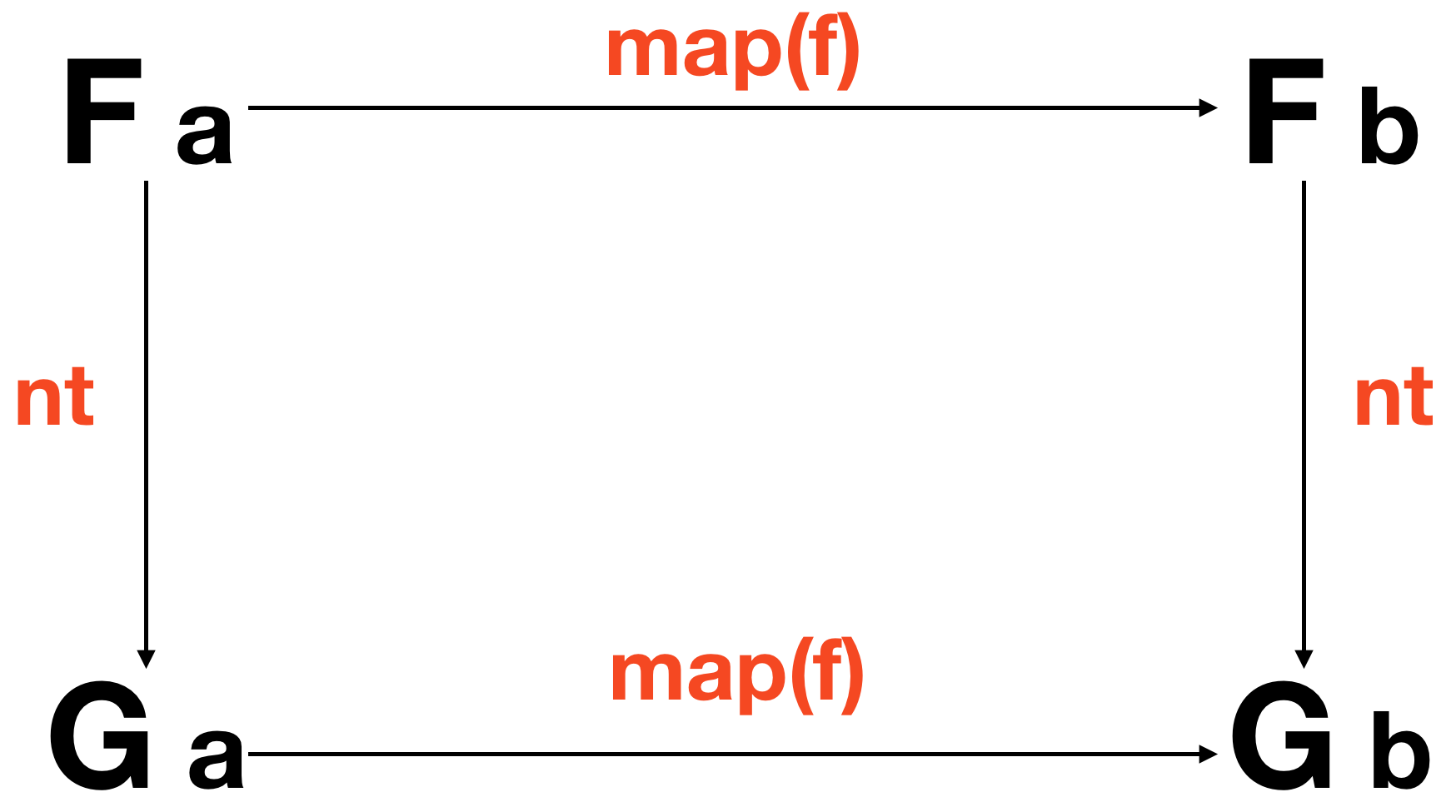
or in code:
// nt :: (Functor f, Functor g) => f a -> g a
compose(map(f), nt) === compose(nt, map(f));
Both the diagram and the code say the same thing: We can run our natural transformation then map or map then run our natural transformation and get the same result. Incidentally, that follows from a free theorem though natural transformations (and functors) are not limited to functions on types.
Principled Type Conversions
As programmers we are familiar with type conversions. We transform types like Strings into Booleans and Integers into Floats (though JavaScript only has Numbers). The difference here is simply that we're working with algebraic containers and we have some theory at our disposal.
Let's look at some of these as examples:
// idToMaybe :: Identity a -> Maybe a
const idToMaybe = x => Maybe.of(x.$value);
// idToIO :: Identity a -> IO a
const idToIO = x => IO.of(x.$value);
// eitherToTask :: Either a b -> Task a b
const eitherToTask = either(Task.rejected, Task.of);
// ioToTask :: IO a -> Task () a
const ioToTask = x => new Task((reject, resolve) => resolve(x.unsafePerform()));
// maybeToTask :: Maybe a -> Task () a
const maybeToTask = x => (x.isNothing ? Task.rejected() : Task.of(x.$value));
// arrayToMaybe :: [a] -> Maybe a
const arrayToMaybe = x => Maybe.of(x[0]);
See the idea? We're just changing one functor to another. We are permitted to lose information along the way so long as the value we'll map doesn't get lost in the shape shift shuffle. That is the whole point: map must carry on, according to our definition, even after the transformation.
One way to look at it is that we are transforming our effects. In that light, we can view ioToTask as converting synchronous to asynchronous or arrayToMaybe from nondeterminism to possible failure. Note that we cannot convert asynchronous to synchronous in JavaScript so we cannot write taskToIO - that would be a supernatural transformation.
Feature Envy
Suppose we'd like to use some features from another type like sortBy on a List. Natural transformations provide a nice way to convert to the target type knowing our map will be sound.
// arrayToList :: [a] -> List a
const arrayToList = List.of;
const doListyThings = compose(sortBy(h), filter(g), arrayToList, map(f));
const doListyThings_ = compose(sortBy(h), filter(g), map(f), arrayToList); // law applied
A wiggle of our nose, three taps of our wand, drop in arrayToList, and voilà! Our [a] is a List a and we can sortBy if we please.
Also, it becomes easier to optimize / fuse operations by moving map(f) to the left of natural transformation as shown in doListyThings_.
Isomorphic JavaScript
When we can completely go back and forth without losing any information, that is considered an isomorphism. That's just a fancy word for "holds the same data". We say that two types are isomorphic if we can provide the "to" and "from" natural transformations as proof:
// promiseToTask :: Promise a b -> Task a b
const promiseToTask = x => new Task((reject, resolve) => x.then(resolve).catch(reject));
// taskToPromise :: Task a b -> Promise a b
const taskToPromise = x => new Promise((resolve, reject) => x.fork(reject, resolve));
const x = Promise.resolve('ring');
taskToPromise(promiseToTask(x)) === x;
const y = Task.of('rabbit');
promiseToTask(taskToPromise(y)) === y;
Q.E.D. Promise and Task are isomorphic. We can also write a listToArray to complement our arrayToList and show that they are too. As a counter example, arrayToMaybe is not an isomorphism since it loses information:
// maybeToArray :: Maybe a -> [a]
const maybeToArray = x => (x.isNothing ? [] : [x.$value]);
// arrayToMaybe :: [a] -> Maybe a
const arrayToMaybe = x => Maybe.of(x[0]);
const x = ['elvis costello', 'the attractions'];
// not isomorphic
maybeToArray(arrayToMaybe(x)); // ['elvis costello']
// but is a natural transformation
compose(arrayToMaybe, map(replace('elvis', 'lou')))(x); // Just('lou costello')
// ==
compose(map(replace('elvis', 'lou'), arrayToMaybe))(x); // Just('lou costello')
They are indeed natural transformations, however, since map on either side yields the same result. I mention isomorphisms here, mid-chapter while we're on the subject, but don't let that fool you, they are an enormously powerful and pervasive concept. Anyways, let's move on.
A Broader Definition
These structural functions aren't limited to type conversions by any means.
Here are a few different ones:
reverse :: [a] -> [a]
join :: (Monad m) => m (m a) -> m a
head :: [a] -> a
of :: a -> f a
The natural transformation laws hold for these functions too. One thing that might trip you up is that head :: [a] -> a can be viewed as head :: [a] -> Identity a. We are free to insert Identity wherever we please whilst proving laws since we can, in turn, prove that a is isomorphic to Identity a (see, I told you isomorphisms were pervasive).
One Nesting Solution
Back to our comedic type signature. We can sprinkle in some natural transformations throughout the calling code to coerce each varying type so they are uniform and, therefore, joinable.
// getValue :: Selector -> Task Error (Maybe String)
// postComment :: String -> Task Error Comment
// validate :: String -> Either ValidationError String
// saveComment :: () -> Task Error Comment
const saveComment = compose(
chain(postComment),
chain(eitherToTask),
map(validate),
chain(maybeToTask),
getValue('#comment'),
);
So what do we have here? We've simply added chain(maybeToTask) and chain(eitherToTask). Both have the same effect; they naturally transform the functor our Task is holding into another Task then join the two. Like pigeon spikes on a window ledge, we avoid nesting right at the source. As they say in the city of light, "Mieux vaut prévenir que guérir" - an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
In Summary
Natural transformations are functions on our functors themselves. They are an extremely important concept in category theory and will start to appear everywhere once more abstractions are adopted, but for now, we've scoped them to a few concrete applications. As we saw, we can achieve different effects by converting types with the guarantee that our composition will hold. They can also help us with nested types, although they have the general effect of homogenizing our functors to the lowest common denominator, which in practice, is the functor with the most volatile effects (Task in most cases).
This continual and tedious sorting of types is the price we pay for having materialized them - summoned them from the ether. Of course, implicit effects are much more insidious and so here we are fighting the good fight. We'll need a few more tools in our tackle before we can reel in the larger type amalgamations. Next up, we'll look at reordering our types with Traversable.
Chapter 12: Traversing the Stone
Exercises
const eitherToMaybe = either(always(nothing), Maybe.of);
/* globals eitherToMaybe */
const just = eitherToMaybe(Either.of('one eyed willy'));
const noth = eitherToMaybe(left('some error'));
assert(
just instanceof Maybe && just.isJust && just.$value === 'one eyed willy',
'The function maps the `Right()` side incorrectly; hint: `Right(14)` should be mapped to `Just(14)`',
);
assert(
noth instanceof Maybe && noth.isNothing,
'The function maps the `Left()` side incorrectly; hint: `Left(\'error\')` should be mapped to `Nothing`',
);
// NOTE We keep named function here to leverage this in the `compose` function,
// and later on in the validations scripts.
/* eslint-disable prefer-arrow-callback */
/* ---------- Internals ---------- */
function namedAs(value, fn) {
Object.defineProperty(fn, 'name', { value });
return fn;
}
// NOTE This file is loaded by gitbook's exercises plugin. When it does, there's an
// `assert` function available in the global scope.
/* eslint-disable no-undef, global-require */
if (typeof assert !== 'function' && typeof require === 'function') {
global.assert = require('assert');
}
assert.arrayEqual = function assertArrayEqual(actual, expected, message = 'arrayEqual') {
if (actual.length !== expected.length) {
throw new Error(message);
}
for (let i = 0; i < expected.length; i += 1) {
if (expected[i] !== actual[i]) {
throw new Error(message);
}
}
};
/* eslint-enable no-undef, global-require */
function inspect(x) {
if (x && typeof x.inspect === 'function') {
return x.inspect();
}
function inspectFn(f) {
return f.name ? f.name : f.toString();
}
function inspectTerm(t) {
switch (typeof t) {
case 'string':
return `'${t}'`;
case 'object': {
const ts = Object.keys(t).map(k => [k, inspect(t[k])]);
return `{${ts.map(kv => kv.join(': ')).join(', ')}}`;
}
default:
return String(t);
}
}
function inspectArgs(args) {
return Array.isArray(args) ? `[${args.map(inspect).join(', ')}]` : inspectTerm(args);
}
return (typeof x === 'function') ? inspectFn(x) : inspectArgs(x);
}
/* eslint-disable no-param-reassign */
function withSpyOn(prop, obj, fn) {
const orig = obj[prop];
let called = false;
obj[prop] = function spy(...args) {
called = true;
return orig.call(this, ...args);
};
fn();
obj[prop] = orig;
return called;
}
/* eslint-enable no-param-reassign */
const typeMismatch = (src, got, fn) => `Type Mismatch in function '${fn}'
${fn} :: ${got}
instead of
${fn} :: ${src}`;
const capitalize = s => `${s[0].toUpperCase()}${s.substring(1)}`;
const ordinal = (i) => {
switch (i) {
case 1:
return '1st';
case 2:
return '2nd';
case 3:
return '3rd';
default:
return `${i}th`; // NOTE won't get any much bigger ...
}
};
const getType = (x) => {
if (x === null) {
return 'Null';
}
if (typeof x === 'undefined') {
return '()';
}
if (Array.isArray(x)) {
return `[${x[0] ? getType(x[0]) : '?'}]`;
}
if (typeof x.getType === 'function') {
return x.getType();
}
if (x.constructor && x.constructor.name) {
return x.constructor.name;
}
return capitalize(typeof x);
};
/* ---------- Essential FP Functions ---------- */
// NOTE A slightly pumped up version of `curry` which also keeps track of
// whether a function was called partially or with all its arguments at once.
// This is useful to provide insights during validation of exercises.
function curry(fn) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
typeMismatch('function -> ?', [getType(fn), '?'].join(' -> '), 'curry'),
);
const arity = fn.length;
return namedAs(fn.name, function $curry(...args) {
$curry.partially = this && this.partially;
if (args.length < arity) {
return namedAs(fn.name, $curry.bind({ partially: true }, ...args));
}
return fn.call(this || { partially: false }, ...args);
});
}
// NOTE A slightly pumped up version of `compose` which also keeps track of the chain
// of callees. In the end, a function created with `compose` holds a `callees` variable
// with the list of all the callees' names.
// This is useful to provide insights during validation of exercises
function compose(...fns) {
const n = fns.length;
return function $compose(...args) {
$compose.callees = [];
let $args = args;
for (let i = n - 1; i >= 0; i -= 1) {
const fn = fns[i];
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
`Invalid Composition: ${ordinal(n - i)} element in a composition isn't a function`,
);
$compose.callees.push(fn.name);
$args = [fn.call(null, ...$args)];
}
return $args[0];
};
}
/* ---------- Algebraic Data Structures ---------- */
class Either {
static of(x) {
return new Right(x); // eslint-disable-line no-use-before-define
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
}
class Left extends Either {
get isLeft() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return true;
}
get isRight() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return false;
}
ap() {
return this;
}
chain() {
return this;
}
inspect() {
return `Left(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Either ${getType(this.$value)} ?)`;
}
join() {
return this;
}
map() {
return this;
}
sequence(of) {
return of(this);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return of(this);
}
}
class Right extends Either {
get isLeft() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return false;
}
get isRight() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return true;
}
ap(f) {
return f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return fn(this.$value);
}
inspect() {
return `Right(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Either ? ${getType(this.$value)})`;
}
join() {
return this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return Either.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
fn(this.$value).map(Either.of);
}
}
class Identity {
static of(x) {
return new Identity(x);
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
ap(f) {
return f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return `Identity(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Identity ${getType(this.$value)})`;
}
join() {
return this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return Identity.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return fn(this.$value).map(Identity.of);
}
}
class IO {
static of(x) {
return new IO(() => x);
}
constructor(io) {
assert(
typeof io === 'function',
'invalid `io` operation given to IO constructor. Use `IO.of` if you want to lift a value in a default minimal IO context.',
);
this.unsafePerformIO = io;
}
ap(f) {
return this.chain(fn => f.map(fn));
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return `IO(${inspect(this.unsafePerformIO())})`;
}
getType() {
return `(IO ${getType(this.unsafePerformIO())})`;
}
join() {
return this.unsafePerformIO();
}
map(fn) {
return new IO(compose(fn, this.unsafePerformIO));
}
}
class Map {
constructor(x) {
assert(
typeof x === 'object' && x !== null,
'tried to create `Map` with non object-like',
);
this.$value = x;
}
inspect() {
return `Map(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
const sample = this.$value[Object.keys(this.$value)[0]];
return `(Map String ${sample ? getType(sample) : '?'})`;
}
insert(k, v) {
const singleton = {};
singleton[k] = v;
return new Map(Object.assign({}, this.$value, singleton));
}
reduce(fn, zero) {
return this.reduceWithKeys((acc, _, k) => fn(acc, k), zero);
}
reduceWithKeys(fn, zero) {
return Object.keys(this.$value)
.reduce((acc, k) => fn(acc, this.$value[k], k), zero);
}
map(fn) {
return new Map(this.reduceWithKeys((obj, v, k) => {
obj[k] = fn(v); // eslint-disable-line no-param-reassign
return obj;
}, {}));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.reduceWithKeys(
(f, a, k) => fn(a).map(b => m => m.insert(k, b)).ap(f),
of(new Map({})),
);
}
}
class List {
static of(x) {
return new List([x]);
}
constructor(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs),
'tried to create `List` from non-array',
);
this.$value = xs;
}
concat(x) {
return new List(this.$value.concat(x));
}
inspect() {
return `List(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
const sample = this.$value[0];
return `(List ${sample ? getType(sample) : '?'})`;
}
map(fn) {
return new List(this.$value.map(fn));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.$value.reduce(
(f, a) => fn(a).map(b => bs => bs.concat(b)).ap(f),
of(new List([])),
);
}
}
class Maybe {
static of(x) {
return new Maybe(x);
}
get isNothing() {
return this.$value === null || this.$value === undefined;
}
get isJust() {
return !this.isNothing;
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
ap(f) {
return this.isNothing ? this : f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return this.isNothing ? 'Nothing' : `Just(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Maybe ${this.isJust ? getType(this.$value) : '?'})`;
}
join() {
return this.isNothing ? this : this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return this.isNothing ? this : Maybe.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.isNothing ? of(this) : fn(this.$value).map(Maybe.of);
}
}
class Task {
constructor(fork) {
assert(
typeof fork === 'function',
'invalid `fork` operation given to Task constructor. Use `Task.of` if you want to lift a value in a default minimal Task context.',
);
this.fork = fork;
}
static of(x) {
return new Task((_, resolve) => resolve(x));
}
static rejected(x) {
return new Task((reject, _) => reject(x));
}
ap(f) {
return this.chain(fn => f.map(fn));
}
chain(fn) {
return new Task((reject, resolve) => this.fork(reject, x => fn(x).fork(reject, resolve)));
}
inspect() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return 'Task(?)';
}
getType() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return '(Task ? ?)';
}
join() {
return this.chain(x => x);
}
map(fn) {
return new Task((reject, resolve) => this.fork(reject, compose(resolve, fn)));
}
}
// In nodejs the existance of a class method named `inspect` will trigger a deprecation warning
// when passing an instance to `console.log`:
// `(node:3845) [DEP0079] DeprecationWarning: Custom inspection function on Objects via .inspect() is deprecated`
// The solution is to alias the existing inspect method with the special inspect symbol exported by node
if (typeof module !== 'undefined' && typeof this !== 'undefined' && this.module !== module) {
const customInspect = require('util').inspect.custom;
const assignCustomInspect = it => it.prototype[customInspect] = it.prototype.inspect;
[Left, Right, Identity, IO, Map, List, Maybe, Task].forEach(assignCustomInspect);
}
const identity = function identity(x) { return x; };
const either = curry(function either(f, g, e) {
if (e.isLeft) {
return f(e.$value);
}
return g(e.$value);
});
const left = function left(x) { return new Left(x); };
const maybe = curry(function maybe(v, f, m) {
if (m.isNothing) {
return v;
}
return f(m.$value);
});
const nothing = Maybe.of(null);
const reject = function reject(x) { return Task.rejected(x); };
const chain = curry(function chain(fn, m) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && typeof m.chain === 'function',
typeMismatch('Monad m => (a -> m b) -> m a -> m a', [getType(fn), getType(m), 'm a'].join(' -> '), 'chain'),
);
return m.chain(fn);
});
const join = function join(m) {
assert(
typeof m.chain === 'function',
typeMismatch('Monad m => m (m a) -> m a', [getType(m), 'm a'].join(' -> '), 'join'),
);
return m.join();
};
const map = curry(function map(fn, f) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && typeof f.map === 'function',
typeMismatch('Functor f => (a -> b) -> f a -> f b', [getType(fn), getType(f), 'f b'].join(' -> '), 'map'),
);
return f.map(fn);
});
const sequence = curry(function sequence(of, x) {
assert(
typeof of === 'function' && typeof x.sequence === 'function',
typeMismatch('(Applicative f, Traversable t) => (a -> f a) -> t (f a) -> f (t a)', [getType(of), getType(x), 'f (t a)'].join(' -> '), 'sequence'),
);
return x.sequence(of);
});
const traverse = curry(function traverse(of, fn, x) {
assert(
typeof of === 'function' && typeof fn === 'function' && typeof x.traverse === 'function',
typeMismatch(
'(Applicative f, Traversable t) => (a -> f a) -> (a -> f b) -> t a -> f (t b)',
[getType(of), getType(fn), getType(x), 'f (t b)'].join(' -> '),
'traverse',
),
);
return x.traverse(of, fn);
});
const unsafePerformIO = function unsafePerformIO(io) {
assert(
io instanceof IO,
typeMismatch('IO a', getType(io), 'unsafePerformIO'),
);
return io.unsafePerformIO();
};
const liftA2 = curry(function liftA2(fn, a1, a2) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function'
&& typeof a1.map === 'function'
&& typeof a2.ap === 'function',
typeMismatch('Applicative f => (a -> b -> c) -> f a -> f b -> f c', [getType(fn), getType(a1), getType(a2)].join(' -> '), 'liftA2'),
);
return a1.map(fn).ap(a2);
});
const liftA3 = curry(function liftA3(fn, a1, a2, a3) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function'
&& typeof a1.map === 'function'
&& typeof a2.ap === 'function'
&& typeof a3.ap === 'function',
typeMismatch('Applicative f => (a -> b -> c -> d) -> f a -> f b -> f c -> f d', [getType(fn), getType(a1), getType(a2)].join(' -> '), 'liftA2'),
);
return a1.map(fn).ap(a2).ap(a3);
});
const always = curry(function always(a, b) { return a; });
/* ---------- Pointfree Classic Utilities ---------- */
const append = curry(function append(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'string' && typeof b === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> String', [getType(a), getType(b), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'concat'),
);
return b.concat(a);
});
const add = curry(function add(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'number' && typeof b === 'number',
typeMismatch('Number -> Number -> Number', [getType(a), getType(b), 'Number'].join(' -> '), 'add'),
);
return a + b;
});
const concat = curry(function concat(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'string' && typeof b === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> String', [getType(a), getType(b), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'concat'),
);
return a.concat(b);
});
const eq = curry(function eq(a, b) {
assert(
getType(a) === getType(b),
typeMismatch('a -> a -> Boolean', [getType(a), getType(b), 'Boolean'].join(' -> '), eq),
);
return a === b;
});
const filter = curry(function filter(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(a -> Boolean) -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(fn), getType(xs), getType(xs)].join(' -> '), 'filter'),
);
return xs.filter(fn);
});
const flip = curry(function flip(fn, a, b) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
typeMismatch('(a -> b) -> (b -> a)', [getType(fn), '(b -> a)'].join(' -> '), 'flip'),
);
return fn(b, a);
});
const forEach = curry(function forEach(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(a -> ()) -> [a] -> ()', [getType(fn), getType(xs), '()'].join(' -> '), 'forEach'),
);
xs.forEach(fn);
});
const intercalate = curry(function intercalate(str, xs) {
assert(
typeof str === 'string' && Array.isArray(xs) && (xs.length === 0 || typeof xs[0] === 'string'),
typeMismatch('String -> [String] -> String', [getType(str), getType(xs), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'intercalate'),
);
return xs.join(str);
});
const head = function head(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string',
typeMismatch('[a] -> a', [getType(xs), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'head'),
);
return xs[0];
};
const last = function last(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string',
typeMismatch('[a] -> a', [getType(xs), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'last'),
);
return xs[xs.length - 1];
};
const match = curry(function match(re, str) {
assert(
re instanceof RegExp && typeof str === 'string',
typeMismatch('RegExp -> String -> Boolean', [getType(re), getType(str), 'Boolean'].join(' -> '), 'match'),
);
return re.test(str);
});
const prop = curry(function prop(p, obj) {
assert(
typeof p === 'string' && typeof obj === 'object' && obj !== null,
typeMismatch('String -> Object -> a', [getType(p), getType(obj), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'prop'),
);
return obj[p];
});
const reduce = curry(function reduce(fn, zero, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(b -> a -> b) -> b -> [a] -> b', [getType(fn), getType(zero), getType(xs), 'b'].join(' -> '), 'reduce'),
);
return xs.reduce(
function $reduceIterator($acc, $x) { return fn($acc, $x); },
zero,
);
});
const safeHead = namedAs('safeHead', compose(Maybe.of, head));
const safeProp = curry(function safeProp(p, obj) { return Maybe.of(prop(p, obj)); });
const sortBy = curry(function sortBy(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('Ord b => (a -> b) -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(fn), getType(xs), '[a]'].join(' -> '), 'sortBy'),
);
return xs.sort((a, b) => {
if (fn(a) === fn(b)) {
return 0;
}
return fn(a) > fn(b) ? 1 : -1;
});
});
const split = curry(function split(s, str) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string' && typeof str === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> [String]', [getType(s), getType(str), '[String]'].join(' -> '), 'split'),
);
return str.split(s);
});
const take = curry(function take(n, xs) {
assert(
typeof n === 'number' && (Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string'),
typeMismatch('Number -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(n), getType(xs), getType(xs)].join(' -> '), 'take'),
);
return xs.slice(0, n);
});
const toLowerCase = function toLowerCase(s) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String', [getType(s), '?'].join(' -> '), 'toLowerCase'),
);
return s.toLowerCase();
};
const toUpperCase = function toUpperCase(s) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String', [getType(s), '?'].join(' -> '), 'toLowerCase'),
);
return s.toUpperCase();
};
/* ---------- Chapter 4 ---------- */
const keepHighest = function keepHighest(x, y) {
try {
keepHighest.calledBy = keepHighest.caller;
} catch (err) {
// NOTE node.js runs in strict mode and prohibit the usage of '.caller'
// There's a ugly hack to retrieve the caller from stack trace.
const [, caller] = /at (\S+)/.exec(err.stack.split('\n')[2]);
keepHighest.calledBy = namedAs(caller, () => {});
}
return x >= y ? x : y;
};
/* ---------- Chapter 5 ---------- */
const cars = [{
name: 'Ferrari FF',
horsepower: 660,
dollar_value: 700000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Spyker C12 Zagato',
horsepower: 650,
dollar_value: 648000,
in_stock: false,
}, {
name: 'Jaguar XKR-S',
horsepower: 550,
dollar_value: 132000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Audi R8',
horsepower: 525,
dollar_value: 114200,
in_stock: false,
}, {
name: 'Aston Martin One-77',
horsepower: 750,
dollar_value: 1850000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Pagani Huayra',
horsepower: 700,
dollar_value: 1300000,
in_stock: false,
}];
const average = function average(xs) {
return xs.reduce(add, 0) / xs.length;
};
/* ---------- Chapter 8 ---------- */
const albert = {
id: 1,
active: true,
name: 'Albert',
address: {
street: {
number: 22,
name: 'Walnut St',
},
},
};
const gary = {
id: 2,
active: false,
name: 'Gary',
address: {
street: {
number: 14,
},
},
};
const theresa = {
id: 3,
active: true,
name: 'Theresa',
};
const yi = { id: 4, name: 'Yi', active: true };
const showWelcome = namedAs('showWelcome', compose(concat('Welcome '), prop('name')));
const checkActive = function checkActive(user) {
return user.active
? Either.of(user)
: left('Your account is not active');
};
const save = function save(user) {
return new IO(() => Object.assign({}, user, { saved: true }));
};
const validateUser = curry(function validateUser(validate, user) {
return validate(user).map(_ => user); // eslint-disable-line no-unused-vars
});
/* ---------- Chapter 9 ---------- */
const getFile = IO.of('/home/mostly-adequate/ch09.md');
const pureLog = function pureLog(str) { return new IO(() => { console.log(str); return str; }); };
const addToMailingList = function addToMailingList(email) { return IO.of([email]); };
const emailBlast = function emailBlast(list) { return IO.of(list.join(',')); };
const validateEmail = function validateEmail(x) {
return /\S+@\S+\.\S+/.test(x)
? Either.of(x)
: left('invalid email');
};
/* ---------- Chapter 10 ---------- */
const localStorage = { player1: albert, player2: theresa };
const game = curry(function game(p1, p2) { return `${p1.name} vs ${p2.name}`; });
const getFromCache = function getFromCache(x) { return new IO(() => localStorage[x]); };
/* ---------- Chapter 11 ---------- */
const findUserById = function findUserById(id) {
switch (id) {
case 1:
return Task.of(Either.of(albert));
case 2:
return Task.of(Either.of(gary));
case 3:
return Task.of(Either.of(theresa));
default:
return Task.of(left('not found'));
}
};
const eitherToTask = namedAs('eitherToTask', either(Task.rejected, Task.of));
/* ---------- Chapter 12 ---------- */
const httpGet = function httpGet(route) { return Task.of(`json for ${route}`); };
const routes = new Map({
'/': '/',
'/about': '/about',
});
const validate = function validate(player) {
return player.name
? Either.of(player)
: left('must have name');
};
const readdir = function readdir(dir) {
return Task.of(['file1', 'file2', 'file3']);
};
const readfile = curry(function readfile(encoding, file) {
return Task.of(`content of ${file} (${encoding})`);
});
/* ---------- Exports ---------- */
if (typeof module === 'object') {
module.exports = {
// Utils
withSpyOn,
// Essential FP helpers
always,
compose,
curry,
either,
identity,
inspect,
left,
liftA2,
liftA3,
maybe,
nothing,
reject,
// Algebraic Data Structures
Either,
IO,
Identity,
Left,
List,
Map,
Maybe,
Right,
Task,
// Currified version of 'standard' functions
append,
add,
chain,
concat,
eq,
filter,
flip,
forEach,
head,
intercalate,
join,
last,
map,
match,
prop,
reduce,
safeHead,
safeProp,
sequence,
sortBy,
split,
take,
toLowerCase,
toUpperCase,
traverse,
unsafePerformIO,
// Chapter 04
keepHighest,
// Chapter 05
cars,
average,
// Chapter 08
albert,
gary,
theresa,
yi,
showWelcome,
checkActive,
save,
validateUser,
// Chapter 09
getFile,
pureLog,
addToMailingList,
emailBlast,
validateEmail,
// Chapter 10
localStorage,
getFromCache,
game,
// Chapter 11
findUserById,
eitherToTask,
// Chapter 12
httpGet,
routes,
validate,
readdir,
readfile,
};
}
// eitherToTask :: Either a b -> Task a b
const eitherToTask = either(Task.rejected, Task.of);
const findNameById = compose(map(prop('name')), chain(eitherToTask), findUserById);
/* globals findNameById */
const throwUnexpected = () => {
throw new Error('The function gives incorrect results; a Task has resolved unexpectedly!');
};
const res = findNameById(1);
assert(
res instanceof Task,
'The function has an incorrect type; hint: `findNameById` must return a `Task String User`!',
);
res.fork(throwUnexpected, (val) => {
assert(
!(val instanceof Task),
'The function has an incorrect type; hint: `findNameById` must return a `Task String User`, make sure to flatten any nested Functor!',
);
assert(
!(val instanceof Either),
'The function has an incorrect type; hint: did you use `eitherToTask` ?',
);
assert(
val === 'Albert',
'The function gives incorrect results for the `Right` side of `Either`.',
);
});
const rej = findNameById(999);
assert(
rej instanceof Task,
'The function has an incorrect type; hint: `findNameById` must return a `Task String User`!',
);
rej.fork((val) => {
assert(
!(val instanceof Task),
'The function has an incorrect type; hint: `findNameById` must return a `Task String User`, make sure to flatten any nested Functor!',
);
assert(
val === 'not found',
'The function gives incorrect results for the `Left` side of `Either`.',
);
}, throwUnexpected);
// NOTE We keep named function here to leverage this in the `compose` function,
// and later on in the validations scripts.
/* eslint-disable prefer-arrow-callback */
/* ---------- Internals ---------- */
function namedAs(value, fn) {
Object.defineProperty(fn, 'name', { value });
return fn;
}
// NOTE This file is loaded by gitbook's exercises plugin. When it does, there's an
// `assert` function available in the global scope.
/* eslint-disable no-undef, global-require */
if (typeof assert !== 'function' && typeof require === 'function') {
global.assert = require('assert');
}
assert.arrayEqual = function assertArrayEqual(actual, expected, message = 'arrayEqual') {
if (actual.length !== expected.length) {
throw new Error(message);
}
for (let i = 0; i < expected.length; i += 1) {
if (expected[i] !== actual[i]) {
throw new Error(message);
}
}
};
/* eslint-enable no-undef, global-require */
function inspect(x) {
if (x && typeof x.inspect === 'function') {
return x.inspect();
}
function inspectFn(f) {
return f.name ? f.name : f.toString();
}
function inspectTerm(t) {
switch (typeof t) {
case 'string':
return `'${t}'`;
case 'object': {
const ts = Object.keys(t).map(k => [k, inspect(t[k])]);
return `{${ts.map(kv => kv.join(': ')).join(', ')}}`;
}
default:
return String(t);
}
}
function inspectArgs(args) {
return Array.isArray(args) ? `[${args.map(inspect).join(', ')}]` : inspectTerm(args);
}
return (typeof x === 'function') ? inspectFn(x) : inspectArgs(x);
}
/* eslint-disable no-param-reassign */
function withSpyOn(prop, obj, fn) {
const orig = obj[prop];
let called = false;
obj[prop] = function spy(...args) {
called = true;
return orig.call(this, ...args);
};
fn();
obj[prop] = orig;
return called;
}
/* eslint-enable no-param-reassign */
const typeMismatch = (src, got, fn) => `Type Mismatch in function '${fn}'
${fn} :: ${got}
instead of
${fn} :: ${src}`;
const capitalize = s => `${s[0].toUpperCase()}${s.substring(1)}`;
const ordinal = (i) => {
switch (i) {
case 1:
return '1st';
case 2:
return '2nd';
case 3:
return '3rd';
default:
return `${i}th`; // NOTE won't get any much bigger ...
}
};
const getType = (x) => {
if (x === null) {
return 'Null';
}
if (typeof x === 'undefined') {
return '()';
}
if (Array.isArray(x)) {
return `[${x[0] ? getType(x[0]) : '?'}]`;
}
if (typeof x.getType === 'function') {
return x.getType();
}
if (x.constructor && x.constructor.name) {
return x.constructor.name;
}
return capitalize(typeof x);
};
/* ---------- Essential FP Functions ---------- */
// NOTE A slightly pumped up version of `curry` which also keeps track of
// whether a function was called partially or with all its arguments at once.
// This is useful to provide insights during validation of exercises.
function curry(fn) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
typeMismatch('function -> ?', [getType(fn), '?'].join(' -> '), 'curry'),
);
const arity = fn.length;
return namedAs(fn.name, function $curry(...args) {
$curry.partially = this && this.partially;
if (args.length < arity) {
return namedAs(fn.name, $curry.bind({ partially: true }, ...args));
}
return fn.call(this || { partially: false }, ...args);
});
}
// NOTE A slightly pumped up version of `compose` which also keeps track of the chain
// of callees. In the end, a function created with `compose` holds a `callees` variable
// with the list of all the callees' names.
// This is useful to provide insights during validation of exercises
function compose(...fns) {
const n = fns.length;
return function $compose(...args) {
$compose.callees = [];
let $args = args;
for (let i = n - 1; i >= 0; i -= 1) {
const fn = fns[i];
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
`Invalid Composition: ${ordinal(n - i)} element in a composition isn't a function`,
);
$compose.callees.push(fn.name);
$args = [fn.call(null, ...$args)];
}
return $args[0];
};
}
/* ---------- Algebraic Data Structures ---------- */
class Either {
static of(x) {
return new Right(x); // eslint-disable-line no-use-before-define
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
}
class Left extends Either {
get isLeft() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return true;
}
get isRight() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return false;
}
ap() {
return this;
}
chain() {
return this;
}
inspect() {
return `Left(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Either ${getType(this.$value)} ?)`;
}
join() {
return this;
}
map() {
return this;
}
sequence(of) {
return of(this);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return of(this);
}
}
class Right extends Either {
get isLeft() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return false;
}
get isRight() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return true;
}
ap(f) {
return f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return fn(this.$value);
}
inspect() {
return `Right(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Either ? ${getType(this.$value)})`;
}
join() {
return this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return Either.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
fn(this.$value).map(Either.of);
}
}
class Identity {
static of(x) {
return new Identity(x);
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
ap(f) {
return f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return `Identity(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Identity ${getType(this.$value)})`;
}
join() {
return this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return Identity.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return fn(this.$value).map(Identity.of);
}
}
class IO {
static of(x) {
return new IO(() => x);
}
constructor(io) {
assert(
typeof io === 'function',
'invalid `io` operation given to IO constructor. Use `IO.of` if you want to lift a value in a default minimal IO context.',
);
this.unsafePerformIO = io;
}
ap(f) {
return this.chain(fn => f.map(fn));
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return `IO(${inspect(this.unsafePerformIO())})`;
}
getType() {
return `(IO ${getType(this.unsafePerformIO())})`;
}
join() {
return this.unsafePerformIO();
}
map(fn) {
return new IO(compose(fn, this.unsafePerformIO));
}
}
class Map {
constructor(x) {
assert(
typeof x === 'object' && x !== null,
'tried to create `Map` with non object-like',
);
this.$value = x;
}
inspect() {
return `Map(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
const sample = this.$value[Object.keys(this.$value)[0]];
return `(Map String ${sample ? getType(sample) : '?'})`;
}
insert(k, v) {
const singleton = {};
singleton[k] = v;
return new Map(Object.assign({}, this.$value, singleton));
}
reduce(fn, zero) {
return this.reduceWithKeys((acc, _, k) => fn(acc, k), zero);
}
reduceWithKeys(fn, zero) {
return Object.keys(this.$value)
.reduce((acc, k) => fn(acc, this.$value[k], k), zero);
}
map(fn) {
return new Map(this.reduceWithKeys((obj, v, k) => {
obj[k] = fn(v); // eslint-disable-line no-param-reassign
return obj;
}, {}));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.reduceWithKeys(
(f, a, k) => fn(a).map(b => m => m.insert(k, b)).ap(f),
of(new Map({})),
);
}
}
class List {
static of(x) {
return new List([x]);
}
constructor(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs),
'tried to create `List` from non-array',
);
this.$value = xs;
}
concat(x) {
return new List(this.$value.concat(x));
}
inspect() {
return `List(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
const sample = this.$value[0];
return `(List ${sample ? getType(sample) : '?'})`;
}
map(fn) {
return new List(this.$value.map(fn));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.$value.reduce(
(f, a) => fn(a).map(b => bs => bs.concat(b)).ap(f),
of(new List([])),
);
}
}
class Maybe {
static of(x) {
return new Maybe(x);
}
get isNothing() {
return this.$value === null || this.$value === undefined;
}
get isJust() {
return !this.isNothing;
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
ap(f) {
return this.isNothing ? this : f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return this.isNothing ? 'Nothing' : `Just(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Maybe ${this.isJust ? getType(this.$value) : '?'})`;
}
join() {
return this.isNothing ? this : this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return this.isNothing ? this : Maybe.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.isNothing ? of(this) : fn(this.$value).map(Maybe.of);
}
}
class Task {
constructor(fork) {
assert(
typeof fork === 'function',
'invalid `fork` operation given to Task constructor. Use `Task.of` if you want to lift a value in a default minimal Task context.',
);
this.fork = fork;
}
static of(x) {
return new Task((_, resolve) => resolve(x));
}
static rejected(x) {
return new Task((reject, _) => reject(x));
}
ap(f) {
return this.chain(fn => f.map(fn));
}
chain(fn) {
return new Task((reject, resolve) => this.fork(reject, x => fn(x).fork(reject, resolve)));
}
inspect() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return 'Task(?)';
}
getType() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return '(Task ? ?)';
}
join() {
return this.chain(x => x);
}
map(fn) {
return new Task((reject, resolve) => this.fork(reject, compose(resolve, fn)));
}
}
// In nodejs the existance of a class method named `inspect` will trigger a deprecation warning
// when passing an instance to `console.log`:
// `(node:3845) [DEP0079] DeprecationWarning: Custom inspection function on Objects via .inspect() is deprecated`
// The solution is to alias the existing inspect method with the special inspect symbol exported by node
if (typeof module !== 'undefined' && typeof this !== 'undefined' && this.module !== module) {
const customInspect = require('util').inspect.custom;
const assignCustomInspect = it => it.prototype[customInspect] = it.prototype.inspect;
[Left, Right, Identity, IO, Map, List, Maybe, Task].forEach(assignCustomInspect);
}
const identity = function identity(x) { return x; };
const either = curry(function either(f, g, e) {
if (e.isLeft) {
return f(e.$value);
}
return g(e.$value);
});
const left = function left(x) { return new Left(x); };
const maybe = curry(function maybe(v, f, m) {
if (m.isNothing) {
return v;
}
return f(m.$value);
});
const nothing = Maybe.of(null);
const reject = function reject(x) { return Task.rejected(x); };
const chain = curry(function chain(fn, m) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && typeof m.chain === 'function',
typeMismatch('Monad m => (a -> m b) -> m a -> m a', [getType(fn), getType(m), 'm a'].join(' -> '), 'chain'),
);
return m.chain(fn);
});
const join = function join(m) {
assert(
typeof m.chain === 'function',
typeMismatch('Monad m => m (m a) -> m a', [getType(m), 'm a'].join(' -> '), 'join'),
);
return m.join();
};
const map = curry(function map(fn, f) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && typeof f.map === 'function',
typeMismatch('Functor f => (a -> b) -> f a -> f b', [getType(fn), getType(f), 'f b'].join(' -> '), 'map'),
);
return f.map(fn);
});
const sequence = curry(function sequence(of, x) {
assert(
typeof of === 'function' && typeof x.sequence === 'function',
typeMismatch('(Applicative f, Traversable t) => (a -> f a) -> t (f a) -> f (t a)', [getType(of), getType(x), 'f (t a)'].join(' -> '), 'sequence'),
);
return x.sequence(of);
});
const traverse = curry(function traverse(of, fn, x) {
assert(
typeof of === 'function' && typeof fn === 'function' && typeof x.traverse === 'function',
typeMismatch(
'(Applicative f, Traversable t) => (a -> f a) -> (a -> f b) -> t a -> f (t b)',
[getType(of), getType(fn), getType(x), 'f (t b)'].join(' -> '),
'traverse',
),
);
return x.traverse(of, fn);
});
const unsafePerformIO = function unsafePerformIO(io) {
assert(
io instanceof IO,
typeMismatch('IO a', getType(io), 'unsafePerformIO'),
);
return io.unsafePerformIO();
};
const liftA2 = curry(function liftA2(fn, a1, a2) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function'
&& typeof a1.map === 'function'
&& typeof a2.ap === 'function',
typeMismatch('Applicative f => (a -> b -> c) -> f a -> f b -> f c', [getType(fn), getType(a1), getType(a2)].join(' -> '), 'liftA2'),
);
return a1.map(fn).ap(a2);
});
const liftA3 = curry(function liftA3(fn, a1, a2, a3) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function'
&& typeof a1.map === 'function'
&& typeof a2.ap === 'function'
&& typeof a3.ap === 'function',
typeMismatch('Applicative f => (a -> b -> c -> d) -> f a -> f b -> f c -> f d', [getType(fn), getType(a1), getType(a2)].join(' -> '), 'liftA2'),
);
return a1.map(fn).ap(a2).ap(a3);
});
const always = curry(function always(a, b) { return a; });
/* ---------- Pointfree Classic Utilities ---------- */
const append = curry(function append(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'string' && typeof b === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> String', [getType(a), getType(b), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'concat'),
);
return b.concat(a);
});
const add = curry(function add(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'number' && typeof b === 'number',
typeMismatch('Number -> Number -> Number', [getType(a), getType(b), 'Number'].join(' -> '), 'add'),
);
return a + b;
});
const concat = curry(function concat(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'string' && typeof b === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> String', [getType(a), getType(b), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'concat'),
);
return a.concat(b);
});
const eq = curry(function eq(a, b) {
assert(
getType(a) === getType(b),
typeMismatch('a -> a -> Boolean', [getType(a), getType(b), 'Boolean'].join(' -> '), eq),
);
return a === b;
});
const filter = curry(function filter(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(a -> Boolean) -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(fn), getType(xs), getType(xs)].join(' -> '), 'filter'),
);
return xs.filter(fn);
});
const flip = curry(function flip(fn, a, b) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
typeMismatch('(a -> b) -> (b -> a)', [getType(fn), '(b -> a)'].join(' -> '), 'flip'),
);
return fn(b, a);
});
const forEach = curry(function forEach(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(a -> ()) -> [a] -> ()', [getType(fn), getType(xs), '()'].join(' -> '), 'forEach'),
);
xs.forEach(fn);
});
const intercalate = curry(function intercalate(str, xs) {
assert(
typeof str === 'string' && Array.isArray(xs) && (xs.length === 0 || typeof xs[0] === 'string'),
typeMismatch('String -> [String] -> String', [getType(str), getType(xs), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'intercalate'),
);
return xs.join(str);
});
const head = function head(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string',
typeMismatch('[a] -> a', [getType(xs), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'head'),
);
return xs[0];
};
const last = function last(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string',
typeMismatch('[a] -> a', [getType(xs), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'last'),
);
return xs[xs.length - 1];
};
const match = curry(function match(re, str) {
assert(
re instanceof RegExp && typeof str === 'string',
typeMismatch('RegExp -> String -> Boolean', [getType(re), getType(str), 'Boolean'].join(' -> '), 'match'),
);
return re.test(str);
});
const prop = curry(function prop(p, obj) {
assert(
typeof p === 'string' && typeof obj === 'object' && obj !== null,
typeMismatch('String -> Object -> a', [getType(p), getType(obj), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'prop'),
);
return obj[p];
});
const reduce = curry(function reduce(fn, zero, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(b -> a -> b) -> b -> [a] -> b', [getType(fn), getType(zero), getType(xs), 'b'].join(' -> '), 'reduce'),
);
return xs.reduce(
function $reduceIterator($acc, $x) { return fn($acc, $x); },
zero,
);
});
const safeHead = namedAs('safeHead', compose(Maybe.of, head));
const safeProp = curry(function safeProp(p, obj) { return Maybe.of(prop(p, obj)); });
const sortBy = curry(function sortBy(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('Ord b => (a -> b) -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(fn), getType(xs), '[a]'].join(' -> '), 'sortBy'),
);
return xs.sort((a, b) => {
if (fn(a) === fn(b)) {
return 0;
}
return fn(a) > fn(b) ? 1 : -1;
});
});
const split = curry(function split(s, str) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string' && typeof str === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> [String]', [getType(s), getType(str), '[String]'].join(' -> '), 'split'),
);
return str.split(s);
});
const take = curry(function take(n, xs) {
assert(
typeof n === 'number' && (Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string'),
typeMismatch('Number -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(n), getType(xs), getType(xs)].join(' -> '), 'take'),
);
return xs.slice(0, n);
});
const toLowerCase = function toLowerCase(s) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String', [getType(s), '?'].join(' -> '), 'toLowerCase'),
);
return s.toLowerCase();
};
const toUpperCase = function toUpperCase(s) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String', [getType(s), '?'].join(' -> '), 'toLowerCase'),
);
return s.toUpperCase();
};
/* ---------- Chapter 4 ---------- */
const keepHighest = function keepHighest(x, y) {
try {
keepHighest.calledBy = keepHighest.caller;
} catch (err) {
// NOTE node.js runs in strict mode and prohibit the usage of '.caller'
// There's a ugly hack to retrieve the caller from stack trace.
const [, caller] = /at (\S+)/.exec(err.stack.split('\n')[2]);
keepHighest.calledBy = namedAs(caller, () => {});
}
return x >= y ? x : y;
};
/* ---------- Chapter 5 ---------- */
const cars = [{
name: 'Ferrari FF',
horsepower: 660,
dollar_value: 700000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Spyker C12 Zagato',
horsepower: 650,
dollar_value: 648000,
in_stock: false,
}, {
name: 'Jaguar XKR-S',
horsepower: 550,
dollar_value: 132000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Audi R8',
horsepower: 525,
dollar_value: 114200,
in_stock: false,
}, {
name: 'Aston Martin One-77',
horsepower: 750,
dollar_value: 1850000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Pagani Huayra',
horsepower: 700,
dollar_value: 1300000,
in_stock: false,
}];
const average = function average(xs) {
return xs.reduce(add, 0) / xs.length;
};
/* ---------- Chapter 8 ---------- */
const albert = {
id: 1,
active: true,
name: 'Albert',
address: {
street: {
number: 22,
name: 'Walnut St',
},
},
};
const gary = {
id: 2,
active: false,
name: 'Gary',
address: {
street: {
number: 14,
},
},
};
const theresa = {
id: 3,
active: true,
name: 'Theresa',
};
const yi = { id: 4, name: 'Yi', active: true };
const showWelcome = namedAs('showWelcome', compose(concat('Welcome '), prop('name')));
const checkActive = function checkActive(user) {
return user.active
? Either.of(user)
: left('Your account is not active');
};
const save = function save(user) {
return new IO(() => Object.assign({}, user, { saved: true }));
};
const validateUser = curry(function validateUser(validate, user) {
return validate(user).map(_ => user); // eslint-disable-line no-unused-vars
});
/* ---------- Chapter 9 ---------- */
const getFile = IO.of('/home/mostly-adequate/ch09.md');
const pureLog = function pureLog(str) { return new IO(() => { console.log(str); return str; }); };
const addToMailingList = function addToMailingList(email) { return IO.of([email]); };
const emailBlast = function emailBlast(list) { return IO.of(list.join(',')); };
const validateEmail = function validateEmail(x) {
return /\S+@\S+\.\S+/.test(x)
? Either.of(x)
: left('invalid email');
};
/* ---------- Chapter 10 ---------- */
const localStorage = { player1: albert, player2: theresa };
const game = curry(function game(p1, p2) { return `${p1.name} vs ${p2.name}`; });
const getFromCache = function getFromCache(x) { return new IO(() => localStorage[x]); };
/* ---------- Chapter 11 ---------- */
const findUserById = function findUserById(id) {
switch (id) {
case 1:
return Task.of(Either.of(albert));
case 2:
return Task.of(Either.of(gary));
case 3:
return Task.of(Either.of(theresa));
default:
return Task.of(left('not found'));
}
};
const eitherToTask = namedAs('eitherToTask', either(Task.rejected, Task.of));
/* ---------- Chapter 12 ---------- */
const httpGet = function httpGet(route) { return Task.of(`json for ${route}`); };
const routes = new Map({
'/': '/',
'/about': '/about',
});
const validate = function validate(player) {
return player.name
? Either.of(player)
: left('must have name');
};
const readdir = function readdir(dir) {
return Task.of(['file1', 'file2', 'file3']);
};
const readfile = curry(function readfile(encoding, file) {
return Task.of(`content of ${file} (${encoding})`);
});
/* ---------- Exports ---------- */
if (typeof module === 'object') {
module.exports = {
// Utils
withSpyOn,
// Essential FP helpers
always,
compose,
curry,
either,
identity,
inspect,
left,
liftA2,
liftA3,
maybe,
nothing,
reject,
// Algebraic Data Structures
Either,
IO,
Identity,
Left,
List,
Map,
Maybe,
Right,
Task,
// Currified version of 'standard' functions
append,
add,
chain,
concat,
eq,
filter,
flip,
forEach,
head,
intercalate,
join,
last,
map,
match,
prop,
reduce,
safeHead,
safeProp,
sequence,
sortBy,
split,
take,
toLowerCase,
toUpperCase,
traverse,
unsafePerformIO,
// Chapter 04
keepHighest,
// Chapter 05
cars,
average,
// Chapter 08
albert,
gary,
theresa,
yi,
showWelcome,
checkActive,
save,
validateUser,
// Chapter 09
getFile,
pureLog,
addToMailingList,
emailBlast,
validateEmail,
// Chapter 10
localStorage,
getFromCache,
game,
// Chapter 11
findUserById,
eitherToTask,
// Chapter 12
httpGet,
routes,
validate,
readdir,
readfile,
};
}
As a reminder, the following functions are available in the exercise's context:
split :: String -> String -> [String]
intercalate :: String -> [String] -> String
const strToList = split('');
const listToStr = intercalate('');
/* globals strToList, listToStr */
const sortLetters = compose(listToStr, sortBy(identity), strToList);
assert(
sortLetters('sortme') === 'emorst',
'The function gives incorrect results',
);
// NOTE We keep named function here to leverage this in the `compose` function,
// and later on in the validations scripts.
/* eslint-disable prefer-arrow-callback */
/* ---------- Internals ---------- */
function namedAs(value, fn) {
Object.defineProperty(fn, 'name', { value });
return fn;
}
// NOTE This file is loaded by gitbook's exercises plugin. When it does, there's an
// `assert` function available in the global scope.
/* eslint-disable no-undef, global-require */
if (typeof assert !== 'function' && typeof require === 'function') {
global.assert = require('assert');
}
assert.arrayEqual = function assertArrayEqual(actual, expected, message = 'arrayEqual') {
if (actual.length !== expected.length) {
throw new Error(message);
}
for (let i = 0; i < expected.length; i += 1) {
if (expected[i] !== actual[i]) {
throw new Error(message);
}
}
};
/* eslint-enable no-undef, global-require */
function inspect(x) {
if (x && typeof x.inspect === 'function') {
return x.inspect();
}
function inspectFn(f) {
return f.name ? f.name : f.toString();
}
function inspectTerm(t) {
switch (typeof t) {
case 'string':
return `'${t}'`;
case 'object': {
const ts = Object.keys(t).map(k => [k, inspect(t[k])]);
return `{${ts.map(kv => kv.join(': ')).join(', ')}}`;
}
default:
return String(t);
}
}
function inspectArgs(args) {
return Array.isArray(args) ? `[${args.map(inspect).join(', ')}]` : inspectTerm(args);
}
return (typeof x === 'function') ? inspectFn(x) : inspectArgs(x);
}
/* eslint-disable no-param-reassign */
function withSpyOn(prop, obj, fn) {
const orig = obj[prop];
let called = false;
obj[prop] = function spy(...args) {
called = true;
return orig.call(this, ...args);
};
fn();
obj[prop] = orig;
return called;
}
/* eslint-enable no-param-reassign */
const typeMismatch = (src, got, fn) => `Type Mismatch in function '${fn}'
${fn} :: ${got}
instead of
${fn} :: ${src}`;
const capitalize = s => `${s[0].toUpperCase()}${s.substring(1)}`;
const ordinal = (i) => {
switch (i) {
case 1:
return '1st';
case 2:
return '2nd';
case 3:
return '3rd';
default:
return `${i}th`; // NOTE won't get any much bigger ...
}
};
const getType = (x) => {
if (x === null) {
return 'Null';
}
if (typeof x === 'undefined') {
return '()';
}
if (Array.isArray(x)) {
return `[${x[0] ? getType(x[0]) : '?'}]`;
}
if (typeof x.getType === 'function') {
return x.getType();
}
if (x.constructor && x.constructor.name) {
return x.constructor.name;
}
return capitalize(typeof x);
};
/* ---------- Essential FP Functions ---------- */
// NOTE A slightly pumped up version of `curry` which also keeps track of
// whether a function was called partially or with all its arguments at once.
// This is useful to provide insights during validation of exercises.
function curry(fn) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
typeMismatch('function -> ?', [getType(fn), '?'].join(' -> '), 'curry'),
);
const arity = fn.length;
return namedAs(fn.name, function $curry(...args) {
$curry.partially = this && this.partially;
if (args.length < arity) {
return namedAs(fn.name, $curry.bind({ partially: true }, ...args));
}
return fn.call(this || { partially: false }, ...args);
});
}
// NOTE A slightly pumped up version of `compose` which also keeps track of the chain
// of callees. In the end, a function created with `compose` holds a `callees` variable
// with the list of all the callees' names.
// This is useful to provide insights during validation of exercises
function compose(...fns) {
const n = fns.length;
return function $compose(...args) {
$compose.callees = [];
let $args = args;
for (let i = n - 1; i >= 0; i -= 1) {
const fn = fns[i];
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
`Invalid Composition: ${ordinal(n - i)} element in a composition isn't a function`,
);
$compose.callees.push(fn.name);
$args = [fn.call(null, ...$args)];
}
return $args[0];
};
}
/* ---------- Algebraic Data Structures ---------- */
class Either {
static of(x) {
return new Right(x); // eslint-disable-line no-use-before-define
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
}
class Left extends Either {
get isLeft() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return true;
}
get isRight() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return false;
}
ap() {
return this;
}
chain() {
return this;
}
inspect() {
return `Left(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Either ${getType(this.$value)} ?)`;
}
join() {
return this;
}
map() {
return this;
}
sequence(of) {
return of(this);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return of(this);
}
}
class Right extends Either {
get isLeft() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return false;
}
get isRight() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return true;
}
ap(f) {
return f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return fn(this.$value);
}
inspect() {
return `Right(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Either ? ${getType(this.$value)})`;
}
join() {
return this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return Either.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
fn(this.$value).map(Either.of);
}
}
class Identity {
static of(x) {
return new Identity(x);
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
ap(f) {
return f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return `Identity(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Identity ${getType(this.$value)})`;
}
join() {
return this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return Identity.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return fn(this.$value).map(Identity.of);
}
}
class IO {
static of(x) {
return new IO(() => x);
}
constructor(io) {
assert(
typeof io === 'function',
'invalid `io` operation given to IO constructor. Use `IO.of` if you want to lift a value in a default minimal IO context.',
);
this.unsafePerformIO = io;
}
ap(f) {
return this.chain(fn => f.map(fn));
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return `IO(${inspect(this.unsafePerformIO())})`;
}
getType() {
return `(IO ${getType(this.unsafePerformIO())})`;
}
join() {
return this.unsafePerformIO();
}
map(fn) {
return new IO(compose(fn, this.unsafePerformIO));
}
}
class Map {
constructor(x) {
assert(
typeof x === 'object' && x !== null,
'tried to create `Map` with non object-like',
);
this.$value = x;
}
inspect() {
return `Map(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
const sample = this.$value[Object.keys(this.$value)[0]];
return `(Map String ${sample ? getType(sample) : '?'})`;
}
insert(k, v) {
const singleton = {};
singleton[k] = v;
return new Map(Object.assign({}, this.$value, singleton));
}
reduce(fn, zero) {
return this.reduceWithKeys((acc, _, k) => fn(acc, k), zero);
}
reduceWithKeys(fn, zero) {
return Object.keys(this.$value)
.reduce((acc, k) => fn(acc, this.$value[k], k), zero);
}
map(fn) {
return new Map(this.reduceWithKeys((obj, v, k) => {
obj[k] = fn(v); // eslint-disable-line no-param-reassign
return obj;
}, {}));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.reduceWithKeys(
(f, a, k) => fn(a).map(b => m => m.insert(k, b)).ap(f),
of(new Map({})),
);
}
}
class List {
static of(x) {
return new List([x]);
}
constructor(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs),
'tried to create `List` from non-array',
);
this.$value = xs;
}
concat(x) {
return new List(this.$value.concat(x));
}
inspect() {
return `List(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
const sample = this.$value[0];
return `(List ${sample ? getType(sample) : '?'})`;
}
map(fn) {
return new List(this.$value.map(fn));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.$value.reduce(
(f, a) => fn(a).map(b => bs => bs.concat(b)).ap(f),
of(new List([])),
);
}
}
class Maybe {
static of(x) {
return new Maybe(x);
}
get isNothing() {
return this.$value === null || this.$value === undefined;
}
get isJust() {
return !this.isNothing;
}
constructor(x) {
this.$value = x;
}
ap(f) {
return this.isNothing ? this : f.map(this.$value);
}
chain(fn) {
return this.map(fn).join();
}
inspect() {
return this.isNothing ? 'Nothing' : `Just(${inspect(this.$value)})`;
}
getType() {
return `(Maybe ${this.isJust ? getType(this.$value) : '?'})`;
}
join() {
return this.isNothing ? this : this.$value;
}
map(fn) {
return this.isNothing ? this : Maybe.of(fn(this.$value));
}
sequence(of) {
return this.traverse(of, x => x);
}
traverse(of, fn) {
return this.isNothing ? of(this) : fn(this.$value).map(Maybe.of);
}
}
class Task {
constructor(fork) {
assert(
typeof fork === 'function',
'invalid `fork` operation given to Task constructor. Use `Task.of` if you want to lift a value in a default minimal Task context.',
);
this.fork = fork;
}
static of(x) {
return new Task((_, resolve) => resolve(x));
}
static rejected(x) {
return new Task((reject, _) => reject(x));
}
ap(f) {
return this.chain(fn => f.map(fn));
}
chain(fn) {
return new Task((reject, resolve) => this.fork(reject, x => fn(x).fork(reject, resolve)));
}
inspect() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return 'Task(?)';
}
getType() { // eslint-disable-line class-methods-use-this
return '(Task ? ?)';
}
join() {
return this.chain(x => x);
}
map(fn) {
return new Task((reject, resolve) => this.fork(reject, compose(resolve, fn)));
}
}
// In nodejs the existance of a class method named `inspect` will trigger a deprecation warning
// when passing an instance to `console.log`:
// `(node:3845) [DEP0079] DeprecationWarning: Custom inspection function on Objects via .inspect() is deprecated`
// The solution is to alias the existing inspect method with the special inspect symbol exported by node
if (typeof module !== 'undefined' && typeof this !== 'undefined' && this.module !== module) {
const customInspect = require('util').inspect.custom;
const assignCustomInspect = it => it.prototype[customInspect] = it.prototype.inspect;
[Left, Right, Identity, IO, Map, List, Maybe, Task].forEach(assignCustomInspect);
}
const identity = function identity(x) { return x; };
const either = curry(function either(f, g, e) {
if (e.isLeft) {
return f(e.$value);
}
return g(e.$value);
});
const left = function left(x) { return new Left(x); };
const maybe = curry(function maybe(v, f, m) {
if (m.isNothing) {
return v;
}
return f(m.$value);
});
const nothing = Maybe.of(null);
const reject = function reject(x) { return Task.rejected(x); };
const chain = curry(function chain(fn, m) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && typeof m.chain === 'function',
typeMismatch('Monad m => (a -> m b) -> m a -> m a', [getType(fn), getType(m), 'm a'].join(' -> '), 'chain'),
);
return m.chain(fn);
});
const join = function join(m) {
assert(
typeof m.chain === 'function',
typeMismatch('Monad m => m (m a) -> m a', [getType(m), 'm a'].join(' -> '), 'join'),
);
return m.join();
};
const map = curry(function map(fn, f) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && typeof f.map === 'function',
typeMismatch('Functor f => (a -> b) -> f a -> f b', [getType(fn), getType(f), 'f b'].join(' -> '), 'map'),
);
return f.map(fn);
});
const sequence = curry(function sequence(of, x) {
assert(
typeof of === 'function' && typeof x.sequence === 'function',
typeMismatch('(Applicative f, Traversable t) => (a -> f a) -> t (f a) -> f (t a)', [getType(of), getType(x), 'f (t a)'].join(' -> '), 'sequence'),
);
return x.sequence(of);
});
const traverse = curry(function traverse(of, fn, x) {
assert(
typeof of === 'function' && typeof fn === 'function' && typeof x.traverse === 'function',
typeMismatch(
'(Applicative f, Traversable t) => (a -> f a) -> (a -> f b) -> t a -> f (t b)',
[getType(of), getType(fn), getType(x), 'f (t b)'].join(' -> '),
'traverse',
),
);
return x.traverse(of, fn);
});
const unsafePerformIO = function unsafePerformIO(io) {
assert(
io instanceof IO,
typeMismatch('IO a', getType(io), 'unsafePerformIO'),
);
return io.unsafePerformIO();
};
const liftA2 = curry(function liftA2(fn, a1, a2) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function'
&& typeof a1.map === 'function'
&& typeof a2.ap === 'function',
typeMismatch('Applicative f => (a -> b -> c) -> f a -> f b -> f c', [getType(fn), getType(a1), getType(a2)].join(' -> '), 'liftA2'),
);
return a1.map(fn).ap(a2);
});
const liftA3 = curry(function liftA3(fn, a1, a2, a3) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function'
&& typeof a1.map === 'function'
&& typeof a2.ap === 'function'
&& typeof a3.ap === 'function',
typeMismatch('Applicative f => (a -> b -> c -> d) -> f a -> f b -> f c -> f d', [getType(fn), getType(a1), getType(a2)].join(' -> '), 'liftA2'),
);
return a1.map(fn).ap(a2).ap(a3);
});
const always = curry(function always(a, b) { return a; });
/* ---------- Pointfree Classic Utilities ---------- */
const append = curry(function append(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'string' && typeof b === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> String', [getType(a), getType(b), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'concat'),
);
return b.concat(a);
});
const add = curry(function add(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'number' && typeof b === 'number',
typeMismatch('Number -> Number -> Number', [getType(a), getType(b), 'Number'].join(' -> '), 'add'),
);
return a + b;
});
const concat = curry(function concat(a, b) {
assert(
typeof a === 'string' && typeof b === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> String', [getType(a), getType(b), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'concat'),
);
return a.concat(b);
});
const eq = curry(function eq(a, b) {
assert(
getType(a) === getType(b),
typeMismatch('a -> a -> Boolean', [getType(a), getType(b), 'Boolean'].join(' -> '), eq),
);
return a === b;
});
const filter = curry(function filter(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(a -> Boolean) -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(fn), getType(xs), getType(xs)].join(' -> '), 'filter'),
);
return xs.filter(fn);
});
const flip = curry(function flip(fn, a, b) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function',
typeMismatch('(a -> b) -> (b -> a)', [getType(fn), '(b -> a)'].join(' -> '), 'flip'),
);
return fn(b, a);
});
const forEach = curry(function forEach(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(a -> ()) -> [a] -> ()', [getType(fn), getType(xs), '()'].join(' -> '), 'forEach'),
);
xs.forEach(fn);
});
const intercalate = curry(function intercalate(str, xs) {
assert(
typeof str === 'string' && Array.isArray(xs) && (xs.length === 0 || typeof xs[0] === 'string'),
typeMismatch('String -> [String] -> String', [getType(str), getType(xs), 'String'].join(' -> '), 'intercalate'),
);
return xs.join(str);
});
const head = function head(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string',
typeMismatch('[a] -> a', [getType(xs), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'head'),
);
return xs[0];
};
const last = function last(xs) {
assert(
Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string',
typeMismatch('[a] -> a', [getType(xs), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'last'),
);
return xs[xs.length - 1];
};
const match = curry(function match(re, str) {
assert(
re instanceof RegExp && typeof str === 'string',
typeMismatch('RegExp -> String -> Boolean', [getType(re), getType(str), 'Boolean'].join(' -> '), 'match'),
);
return re.test(str);
});
const prop = curry(function prop(p, obj) {
assert(
typeof p === 'string' && typeof obj === 'object' && obj !== null,
typeMismatch('String -> Object -> a', [getType(p), getType(obj), 'a'].join(' -> '), 'prop'),
);
return obj[p];
});
const reduce = curry(function reduce(fn, zero, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('(b -> a -> b) -> b -> [a] -> b', [getType(fn), getType(zero), getType(xs), 'b'].join(' -> '), 'reduce'),
);
return xs.reduce(
function $reduceIterator($acc, $x) { return fn($acc, $x); },
zero,
);
});
const safeHead = namedAs('safeHead', compose(Maybe.of, head));
const safeProp = curry(function safeProp(p, obj) { return Maybe.of(prop(p, obj)); });
const sortBy = curry(function sortBy(fn, xs) {
assert(
typeof fn === 'function' && Array.isArray(xs),
typeMismatch('Ord b => (a -> b) -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(fn), getType(xs), '[a]'].join(' -> '), 'sortBy'),
);
return xs.sort((a, b) => {
if (fn(a) === fn(b)) {
return 0;
}
return fn(a) > fn(b) ? 1 : -1;
});
});
const split = curry(function split(s, str) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string' && typeof str === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String -> [String]', [getType(s), getType(str), '[String]'].join(' -> '), 'split'),
);
return str.split(s);
});
const take = curry(function take(n, xs) {
assert(
typeof n === 'number' && (Array.isArray(xs) || typeof xs === 'string'),
typeMismatch('Number -> [a] -> [a]', [getType(n), getType(xs), getType(xs)].join(' -> '), 'take'),
);
return xs.slice(0, n);
});
const toLowerCase = function toLowerCase(s) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String', [getType(s), '?'].join(' -> '), 'toLowerCase'),
);
return s.toLowerCase();
};
const toUpperCase = function toUpperCase(s) {
assert(
typeof s === 'string',
typeMismatch('String -> String', [getType(s), '?'].join(' -> '), 'toLowerCase'),
);
return s.toUpperCase();
};
/* ---------- Chapter 4 ---------- */
const keepHighest = function keepHighest(x, y) {
try {
keepHighest.calledBy = keepHighest.caller;
} catch (err) {
// NOTE node.js runs in strict mode and prohibit the usage of '.caller'
// There's a ugly hack to retrieve the caller from stack trace.
const [, caller] = /at (\S+)/.exec(err.stack.split('\n')[2]);
keepHighest.calledBy = namedAs(caller, () => {});
}
return x >= y ? x : y;
};
/* ---------- Chapter 5 ---------- */
const cars = [{
name: 'Ferrari FF',
horsepower: 660,
dollar_value: 700000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Spyker C12 Zagato',
horsepower: 650,
dollar_value: 648000,
in_stock: false,
}, {
name: 'Jaguar XKR-S',
horsepower: 550,
dollar_value: 132000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Audi R8',
horsepower: 525,
dollar_value: 114200,
in_stock: false,
}, {
name: 'Aston Martin One-77',
horsepower: 750,
dollar_value: 1850000,
in_stock: true,
}, {
name: 'Pagani Huayra',
horsepower: 700,
dollar_value: 1300000,
in_stock: false,
}];
const average = function average(xs) {
return xs.reduce(add, 0) / xs.length;
};
/* ---------- Chapter 8 ---------- */
const albert = {
id: 1,
active: true,
name: 'Albert',
address: {
street: {
number: 22,
name: 'Walnut St',
},
},
};
const gary = {
id: 2,
active: false,
name: 'Gary',
address: {
street: {
number: 14,
},
},
};
const theresa = {
id: 3,
active: true,
name: 'Theresa',
};
const yi = { id: 4, name: 'Yi', active: true };
const showWelcome = namedAs('showWelcome', compose(concat('Welcome '), prop('name')));
const checkActive = function checkActive(user) {
return user.active
? Either.of(user)
: left('Your account is not active');
};
const save = function save(user) {
return new IO(() => Object.assign({}, user, { saved: true }));
};
const validateUser = curry(function validateUser(validate, user) {
return validate(user).map(_ => user); // eslint-disable-line no-unused-vars
});
/* ---------- Chapter 9 ---------- */
const getFile = IO.of('/home/mostly-adequate/ch09.md');
const pureLog = function pureLog(str) { return new IO(() => { console.log(str); return str; }); };
const addToMailingList = function addToMailingList(email) { return IO.of([email]); };
const emailBlast = function emailBlast(list) { return IO.of(list.join(',')); };
const validateEmail = function validateEmail(x) {
return /\S+@\S+\.\S+/.test(x)
? Either.of(x)
: left('invalid email');
};
/* ---------- Chapter 10 ---------- */
const localStorage = { player1: albert, player2: theresa };
const game = curry(function game(p1, p2) { return `${p1.name} vs ${p2.name}`; });
const getFromCache = function getFromCache(x) { return new IO(() => localStorage[x]); };
/* ---------- Chapter 11 ---------- */
const findUserById = function findUserById(id) {
switch (id) {
case 1:
return Task.of(Either.of(albert));
case 2:
return Task.of(Either.of(gary));
case 3:
return Task.of(Either.of(theresa));
default:
return Task.of(left('not found'));
}
};
const eitherToTask = namedAs('eitherToTask', either(Task.rejected, Task.of));
/* ---------- Chapter 12 ---------- */
const httpGet = function httpGet(route) { return Task.of(`json for ${route}`); };
const routes = new Map({
'/': '/',
'/about': '/about',
});
const validate = function validate(player) {
return player.name
? Either.of(player)
: left('must have name');
};
const readdir = function readdir(dir) {
return Task.of(['file1', 'file2', 'file3']);
};
const readfile = curry(function readfile(encoding, file) {
return Task.of(`content of ${file} (${encoding})`);
});
/* ---------- Exports ---------- */
if (typeof module === 'object') {
module.exports = {
// Utils
withSpyOn,
// Essential FP helpers
always,
compose,
curry,
either,
identity,
inspect,
left,
liftA2,
liftA3,
maybe,
nothing,
reject,
// Algebraic Data Structures
Either,
IO,
Identity,
Left,
List,
Map,
Maybe,
Right,
Task,
// Currified version of 'standard' functions
append,
add,
chain,
concat,
eq,
filter,
flip,
forEach,
head,
intercalate,
join,
last,
map,
match,
prop,
reduce,
safeHead,
safeProp,
sequence,
sortBy,
split,
take,
toLowerCase,
toUpperCase,
traverse,
unsafePerformIO,
// Chapter 04
keepHighest,
// Chapter 05
cars,
average,
// Chapter 08
albert,
gary,
theresa,
yi,
showWelcome,
checkActive,
save,
validateUser,
// Chapter 09
getFile,
pureLog,
addToMailingList,
emailBlast,
validateEmail,
// Chapter 10
localStorage,
getFromCache,
game,
// Chapter 11
findUserById,
eitherToTask,
// Chapter 12
httpGet,
routes,
validate,
readdir,
readfile,
};
}